Trypanosoma cruzi causes Chagas’ disease. The reservoir includes many wild animals. The vector is reduviid, the “kissing bug.”
Xenodiagnosis allows for the identification of trypanosomes in the intestinal tract of the reduviid bug, which confirms the diagnosis.
Trypanosoma cruzi
Toxoplasmosis
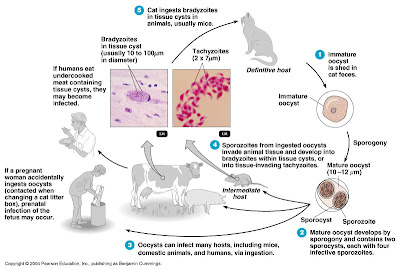
Toxoplasmosis is caused by the sporozoan Toxoplasma gondii.
T. gondii undergoes sexual reproduction in the intestinal tract of domestic cats (the reservoir), and oocysts are eliminated in cat feces.
In the host cell, sporozoites reproduce to form either tissue invading tachyzoites or bradyzoites.
Humans contract the infection by ingesting tachyzoites or tissue cysts in undercooked meat from an infected animal or contact with cat feces (transmission is gastrointestinal).
Congenital infections can occur. Signs and symptoms include severe brain damage or vision problems.
Toxoplasmosis can be identified by serological tests, but interpretation of the results is uncertain.
Malaria
The signs and symptoms of malaria are chills, fever, vomiting, and headache, which occur at intervals of 2-3 days.
Malaria is transmitted by Anopheles mosquitoes. The causative agent is any one of four species of Plasmodium.
Sporozoites reproduced in the liver and release merozoites into the blood stream, where they infect red blood cells and produce more merozoites.
Laboratory diagnosis is based on microscopic observation of merozoites in red blood cells.
New drugs are being developed as the protozoa develop resistance to drugs such as chloroquine.
Malaria in the United States
Malaria
Leishmaniasis
Leishmania spp., which are transmitted by sandflies, cause leishmaniasis.
Leishmania donovani - visceral leishmaniasis: the protozoa reproduce in the liver, spleen and kidneys.
Leishmania tropica - cutaneous leishmaniasis (Oriental sore): affects skin
Leishmania braziliensis - mucocutaneous leishmaniasis: affects mucous membranes as well as skin
Antimony compounds are used for treatment.
Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
Babesiosis
Babesiosis is caused by the protozoan Babesia microti and transmitted to humans by ticks.
Helminthic Diseases of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
Schistosomiasis
Species of the blood fluke Schistosoma cause schistosomiasis.
Eggs eliminated with feces hatch into larvae that infect the intermediate host, a snail. Free-swimming cercariae are released from the snail and penetrate the skin of a human.
The adult flukes live in the veins of the liver or urinary bladder in humans.
Granulomas are from the host’s defense against eggs that remain in the body.
Observation of eggs or flukes in feces, skin tests, or indirect serological tests may be used for diagnosis.
Chemotherapy (praziquantel or oxamniquine) is used to treat the disease; sanitation and snail eradication are used to prevent it.
Schistosomiasis
Schistosome Granuloma
Swimmer’s Itch
Swimmer’s itch is a cutaneous allergic reaction to cercariae that penetrate the skin. The definitive hosts for this fluke are wildfowl.